Financial technology has become immensely popular thanks to the increased number of applications and use cases of fintech services.
People today use their smartphones to make payments, manage their bank accounts, and finish other financial transactions, which gives a clear picture of how impactful the implementation of fintech has been.
Looking at this rapid growth in demand, there are several non-banking service providers that have shown interest in entering the fintech realm.
And powering them in the backend is banking as a service, popularly known as BaaS. It serves as the powerhouse of non-banking organizations, allowing them to offer banking services.
While the rise of banking as a service has powered growth in multiple sectors and businesses, it is still a point of confusion for many, as they do not understand exactly what banking as a service means.
If you, too, are struggling with the same, then this post is certainly for you!
In this article, let’s take a closer look at banking as a service, or BaaS, as a concept and explore everything there is to know about it. Without further ado, let’s get started!
What is Banking as a Service?
Banking as a service is a concept that allows a business to enter the growing fintech space without having to fundamentally enter the banking realm, take a license, or build a dedicated infrastructure to support banking services.

Let’s understand this with an example:
Suppose you are an emerging startup that helps make online payments accessible. To enter the payments market, you will need banking connectivity; otherwise, where do you deposit the funds from the wallet?
This introduces several challenges, as while your main goal is to revolutionize the payments sector, you will have to go through all the hassle that it takes to gain licenses and meet banking regulatory requirements.
Now, with banking as a service, you will not have to worry about all of that, as you can simply opt for BaaS and get your hands on the banking infrastructure of an existing bank. Which means no licensing, no hassle, nothing.
And that is how banking as a service functions. BaaS is certainly the best chance for any non-financial service provider to enter the banking sector without having to invest a lot and work on building a well-developed infrastructure for banking services.
Mechanism of BaaS API: How it All Works?
Banking as a Service is enabled with the use of APIs that allow companies to leverage required functionalities directly from the bank without building an infrastructure of their own.
The core benefits of using Banking as a Service APIs are that they save businesses the hassle and time that goes into acquiring the required infrastructure, licenses, and regulatory requirements.
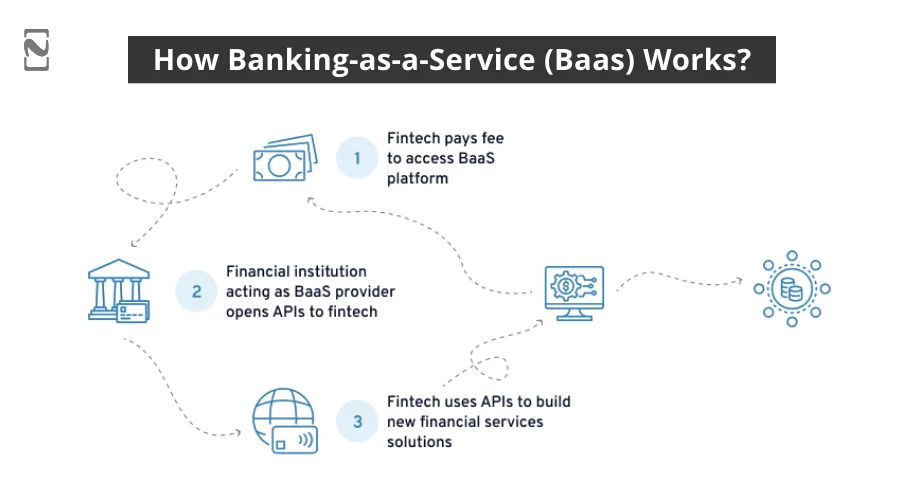
The banks take care of it, and they can easily borrow it all through BaaS APIs. However, it is not that simple.
You see, there are several parties involved in the overall solution.
There are:
- Banks, which enable banks to offer banking as a service,
- Technical experts, who help in API integration for non-banking organizations to leverage banking solutions, and
- Lastly, the app developers, who create an app for the final solution that wants to use BaaS.
What this means is that banks that want to extend their services to the non-banking tech companies planning to enter the fintech market can offer an open API that these non-banking businesses can leverage to access financial services and features, including payments, loans, account creation, and more.
All these features are integrated through modular BaaS APIs. The modular nature of these banking-as-a-service APIs allows the business to pick and choose the features that it wants to integrate. This also means it is not necessary for a business to invest in complete banking services.
How BaaS is Different Than Other Types of Banking Solutions?
People often confuse banking as a service with embedded finance, & open banking, as these are also concepts that allow businesses to offer financial services in a non-financial platform.
However, the difference between them is significant as one offers a backend to function while the other is more on the frontend. To understand the concepts better, here is a quick comparison between all of them.
► Embedded Finance vs BaaS
Embedded Finance integrates financial services into non-financial platforms, enhancing the user experience by offering seamless transactions and financial operations within the app.
Banking as a Service (BaaS), on the other hand, allows non-banks to offer banking services using the infrastructure of traditional banks.
| Features | Embedded Finance | Banking as a Service (BaaS) |
| 1. Integration | Financial services within existing apps | Non-banks use banking infrastructure |
| 2. User Experience | Enhanced and seamless transactions | Customizable financial service offerings |
| 3. Main Providers | Tech companies and e-commerce platforms | Traditional banks offering their infrastructure |
► Open Banking vs BaaS
Open Banking APIs allow third-party developers to access banking data and services to create innovative financial solutions.
Banking as a Service (BaaS) extends this by enabling third parties to offer full-fledged banking services by using the infrastructure of existing banks.
| Features | Open Banking | Banking as a Service (BaaS) |
| 1. Data Access | Access customer data via APIs | Access to complete banking services |
| 2. Innovation | Focus on new financial products | Focus on integrating existing banking services |
| 3. Regulation | Strong regulatory oversight | Compliance with banking regulations |
What Methods Can be Used to Implement BaaS?
Now that you are aware of how banking as a service is different from embedded banking or open banking, you may be wondering how the concept can be integrated into a non-banking environment.
Or in simple words, how BaaS establishes a connection between traditional banks and non-banking solutions that need help with the banking infrastructure.
The whole idea is to connect the two in such a way that the backend services related to banking are done through a traditional bank, without the user having to go through all of that.
The integration is done through the following methods:
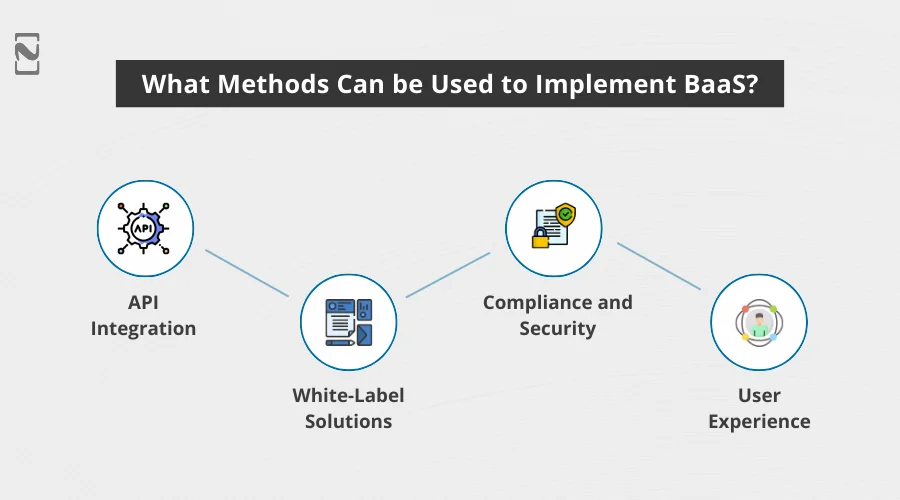
1] API Integration
Banks provide Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that allow third-party companies to integrate and access various banking services such as account management, payments, and lending.
These APIs act as a bridge, enabling non-banking businesses to connect with the bank’s core systems efficiently and securely.
2] White-Label Solutions
Non-banking entities can rebrand and offer these banking services under their name. This means a fintech company can provide banking products like digital wallets, credit cards, or loans without having to build the backend systems.
Companies have the flexibility to tailor the user interface and experience to match their brand’s look and feel, ensuring a seamless integration of banking services within their existing platforms.
By integrating banking services directly into their platforms, they can offer customers a more streamlined and convenient way to access financial products, providing a superior customer experience.
This setup allows for rapid innovation. Companies can quickly roll out new features and services without the need for extensive development cycles.
In essence, Banking as a Service allows businesses to leverage the robust infrastructure of established banks to offer financial services. The majority of non-banking businesses tend to use BaaS APIs as these are more impactful and require less effort /
This results in a faster go-to-market strategy for new financial products and a more diverse range of services for consumers.
Benefits of Using BaaS APIs on Your Platform!
Now that you are aware of how things work and what the ways are, you can utilize BaaS. It is time to take a look at some of the factors that prove to be beneficial for the success of your venture.
You see, there are multiple benefits that you can enjoy if you build a BaaS platform.
Some of these benefits include:
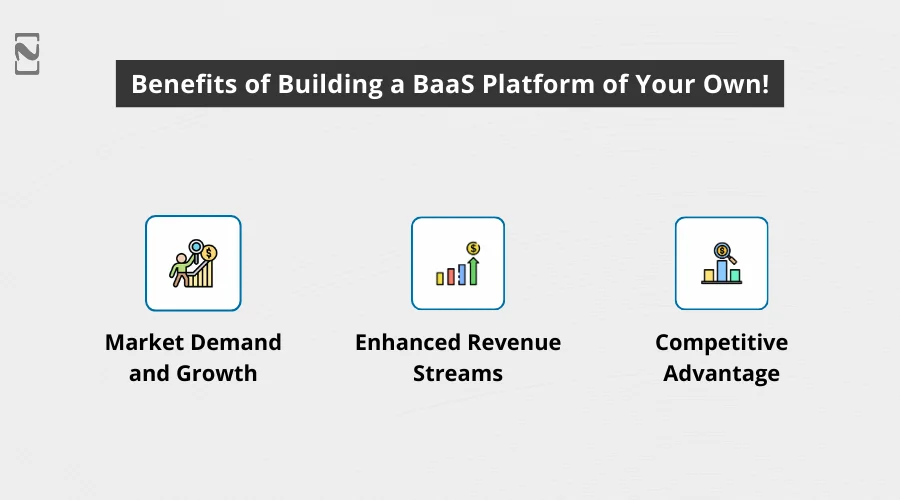
1. Market Demand and Growth
The demand for banking as a service is rapidly increasing. Fintech Statistics shows that the global BaaS market size was valued at $716 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $1802.61 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 21.2% from 2025 to 2029.
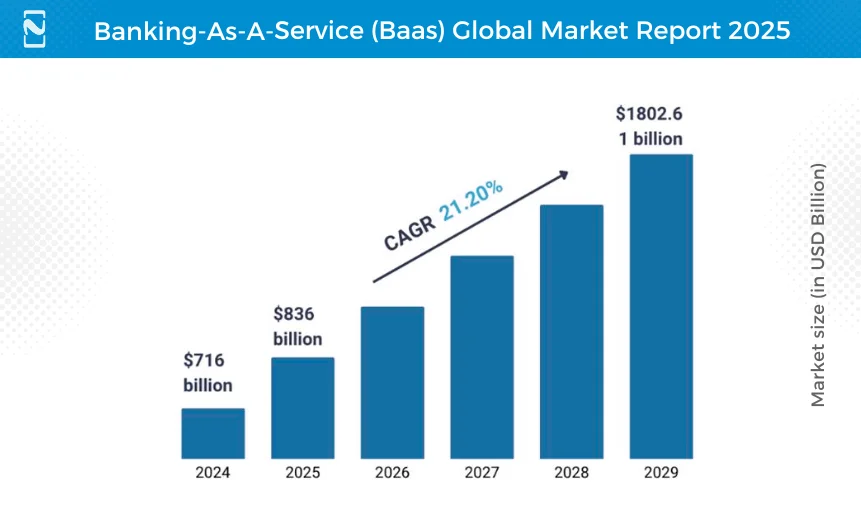
This explosive growth highlights substantial market opportunities for fintech companies. With the help of the BaaS API, you can tap into this expanding market, offering innovative financial solutions that cater to the evolving needs of businesses and consumers.
2. Enhanced Revenue Streams
Fintech makes a lot of money! And that’s precisely a reason to go for it.
BaaS API allows non-banking fintech companies to create new revenue streams.
According to Deloitte, financial institutions that leverage BaaS can see up to a 50% increase in their revenue growth rate.
By providing banking services to other businesses, fintech firms can charge for API usage, transaction fees, and premium services.
This diversification of income sources not only boosts profitability but also provides a more stable financial foundation, reducing reliance on a single revenue stream.
3. Compliance and Security
Banks handle all regulatory compliance, ensuring that third-party services adhere to financial regulations and standards.
This includes KYC (Know Your Customer), AML (Anti-Money Laundering), and other regulatory requirements. Banks also manage the security aspects, protecting sensitive customer data through advanced encryption and security protocols.
4. Competitive Advantage
BaaS API integration positions your company at the forefront of financial innovation and makes it popular among the target audience.
According to a McKinsey report, companies that adopt BaaS APIs can reduce their time to market by up to 60%. This agility enables you to respond quickly to market trends and customer demands, giving you a significant edge over competitors who rely on traditional banking infrastructure.
Moreover, BaaS can attract partnerships with other fintech companies and businesses seeking to integrate banking services, further solidifying your market position and expanding your network.
Banking as a service development can open up substantial opportunities for fintech companies, driving growth, revenue, and competitive advantage.
By leveraging growing demand, creating new revenue streams, and staying ahead of the competition, your fintech business can thrive in the rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Steps to Develop a Banking-as-a-Service Platform
Just like any other business, you need to have a set process that helps you finish the development of a banking-as-a-service platform. A series of steps can take you towards a well-designed solution.
If you plan to enter the market with a banking-as-a-service platform, check out the following steps that define the process of building a BaaS solution:
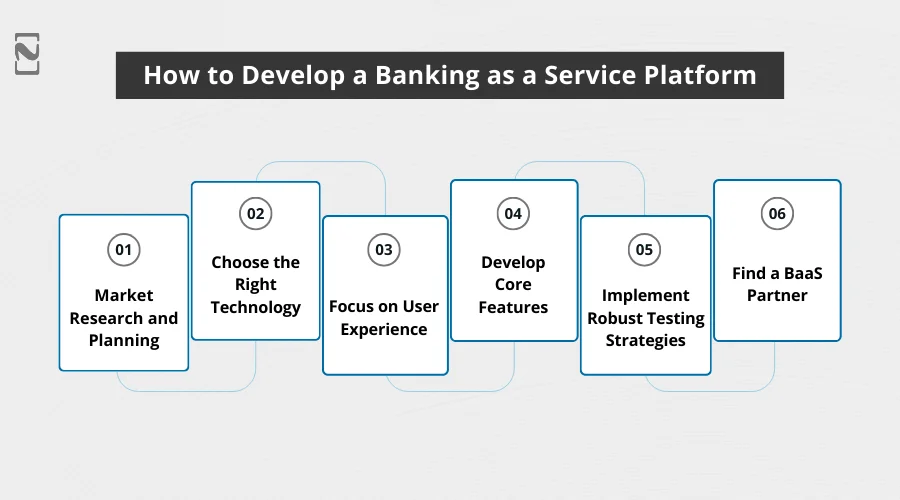
Step 1: Market Research and Planning
Identify market opportunities by researching the market thoroughly. You can find multiple insights about banking services that are relevant to your idea of building an app using BaaS.
Pick the features that will be required to build an app related to your niche, be it lending, payments, or anything else.
This is the stage where you plan and establish the goals that you plan to achieve, including your target audience, market positioning, and revenue models.
Step 2: Choose the Right Technology
If you are building a fintech solution while using banking as a service, you have to be diligent about the technology stack that you choose.
A lot of technology is involved in building the solution that you need. It is advised that you opt for an API-first architecture that facilitates easy integration and supports easy scalability in the long run.
You should also focus on ensuring the security of your solution, choosing measures that not only keep things secure but also meet regulatory requirements and compliance.
Step 3: Focus on User Experience
User experience is one of the most crucial sections of your app as it decides how a user interacts with your service.
Design an intuitive and user-friendly interface that provides a seamless experience for both end-users and business clients.
Prioritize accessibility and ease of use, ensuring that users can navigate and utilize your platform effortlessly.
This is also the step where you define the flow of your application features, so make sure you pay attention to it and focus accordingly.
Step 4: Find a BaaS Partner
After you have identified the design and experience for your app, it is time to identify the right banking as a service provider, whose BaaS API you would like to use.
Keep in mind that at the end of the day, it is your provider who serves as the backbone. Hence, choosing the right BaaS partner is crucial.
What helps in choosing the right partner is looking for their market reviews related to compliance and pricing that they use.
You do have the option of asking potential partners for demos to ensure that the BaaS API you choose is functional and can be simplified. Simply identify the key features/functionalities you need and what the service costs relative to the same before making your decision.
Step 5: Integrate APIs and Develop Functionalities
After you have chosen the BaaS API that will power your financial platform, it is time to integrate it into the system. Develop functionalities and integrate the BaaS API into it to establish a BaaS-enabled system.
This is the step where you send a request for authorization for handling transactions within your platform. Make sure that the integration of the BaaS API is done after due diligence related to compliance practices.
That is because, while the bank that is offering BaaS sorts out all the necessary licenses for you, it is your responsibility to maintain the integrity of regulations and compliance. Pay extra attention to these aspects when building a platform using BaaS APIs.
Step 6: Implement Robust Testing Strategies
Lastly, when the application is developed, make sure that it is functioning properly. The idea is to ensure that the app is free of bugs, does what it was intended to do, and can function under different circumstances.
This is also the step where you can ensure that the application you have built is compliant and follows all the necessary regulatory requirements.
You can even finish testing the app for different test cases in this step to be more confident that the BaaS has been integrated properly and there are no problems.
With these steps, you can easily build a fintech app by integrating the BaaS API. Banking as a service requires you to partner with companies that offer their infrastructure for you. Choosing the right BaaS API can only help when you have completed the process thoroughly.
In order to make the most of your integration, you need an experienced partner who can help you finish the application development process along with BaaS API integration.
Building an in-house team can be time-consuming and expensive. If you are looking for a solution, you will need a fintech app development company to guide you through the process of BaaS API integration.
Nimble AppGenie: Driving Innovation With Banking as a Service
Now that you have identified the top banking as a service provider in the market, half of your concern is resolved, as you can look for the key features and choose accordingly.
For the other half, you need to find professional fintech app development services that not only identify the goals but also do all the technical integrations for you.
If you are looking for a development partner, we highly recommend choosing Nimble AppGenie, as they have years of experience.
Being a pioneer in the fintech development industry, the brand has helped significant banking businesses to make an impact in the industry with their smartly curated, technically advanced fintech solutions.
Connect with the experts today and start building your application with BaaS support.
Banking as a service is a key player in helping businesses and entrepreneurs from non-banking backgrounds to enter the fintech market. Capitalize on this opportunity with Nimble AppGenie for the best results!
Conclusion
Banking as a Service (BaaS) represents a transformative shift in the financial landscape, offering fintech companies the tools to innovate and scale rapidly.
By leveraging the infrastructure of established banks, businesses can provide diverse financial services, enhance user experiences, and stay compliant with regulatory requirements.
The future of BaaS and fintech apps is bright, with emerging trends like AI, blockchain, and embedded finance driving further advancements.
As the market continues to grow, developing a robust BaaS platform can position your company at the forefront of financial innovation and customer satisfaction.
Hopefully, you now have a clear idea of what BaaS is and how you can implement it to build an efficient and reliable system.
In case you are worried about development requirements, feel free to connect with the experts. That will be all for this one.
FAQs
Banking as a Service (BaaS) is a model where banks offer their infrastructure to third-party businesses via APIs, enabling them to provide financial services without building their own banking systems.
BaaS allows non-banking entities to offer banking services using the infrastructure of established banks, whereas traditional banking involves banks providing these services directly to customers.
BaaS offers cost efficiency, faster time to market, scalability, enhanced innovation, regulatory compliance, improved security, customizable user experience, and more.
The development cost for a BaaS platform ranges from $500K to $2 million, depending on factors like technology stack, regulatory compliance, and feature development.
Some top BaaS providers include Solarisbank, Railsbank, Bankable, FintechOS, Mambu, Fidor Solutions, and Synapse.
BaaS providers handle regulatory compliance by adhering to financial regulations such as KYC and AML, ensuring that all services meet necessary legal standards.
Key trends include AI and machine learning integration, blockchain technology, open banking expansion, embedded finance, digital identity verification, and more.
BaaS platforms are highly scalable, allowing for easy adjustments based on demand.
BaaS platforms implement advanced security measures such as encryption, secure authentication, and continuous monitoring to protect sensitive customer data.
Start by conducting market research, ensuring regulatory compliance, choosing the right technology, partnering with banks, developing core features, and focusing on user experience.

Niketan Sharma, CTO, Nimble AppGenie, is a tech enthusiast with more than a decade of experience in delivering high-value solutions that allow a brand to penetrate the market easily. With a strong hold on mobile app development, he is actively working to help businesses identify the potential of digital transformation by sharing insightful statistics, guides & blogs.
Table of Contents


No Comments
Comments are closed.